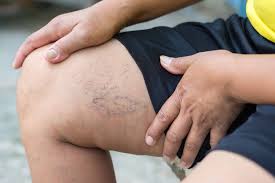
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in one or more deep veins, often in the legs. While it can present with symptoms such as pain or swelling, some individuals remain asymptomatic, highlighting the need for awareness. Individuals with DVT may face potential complications, including pulmonary embolism, which occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs. Understanding the risks, causes, and strategies to prevent DVT can help individuals take proactive steps to reduce its likelihood.
Understanding Risks and Common Causes
Several factors increase the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis. Prolonged immobility is among the most prominent, frequently associated with long flights, extended bed rest, or hospital stays. Reduced mobility decreases blood flow, promoting clot formation. Other risk factors include conditions affecting blood clotting, such as thrombophilia or cancer, and lifestyle factors like smoking, which increases clotting tendencies.
Surgical procedures, particularly orthopedic surgeries, also heighten this risk due to prolonged immobility during recovery. Pregnancy can similarly result in increased risk because of pressure on the pelvic veins combined with hormonal changes that promote clot formation. Anyone with prior incidents of venous thrombosis or a family history of the condition also faces elevated susceptibility.
Recognizing Symptoms and Complications
Recognizing signs of DVT is paramount in addressing it early. Common symptoms include swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected limb, paired with pain or tenderness often concentrated in the calf. While symptoms typically manifest in one leg, they may not always appear, complicating detection.
Complications arise when untreated blood clots dislodge and travel through the bloodstream. Pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition, occurs when a clot blocks a lung artery. Symptoms of pulmonary embolism include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid heart rate, and dizziness. Seeking immediate medical attention upon noticing such symptoms can significantly reduce severe outcomes.
Preventing DVT
Prevention strategies for DVT focus on maintaining healthy blood circulation and reducing clotting risks. Regular movement plays a role, especially during periods of prolonged sitting or standing. Individuals taking long flights or sitting at desks for extended hours benefit from frequent leg exercises, stretches, or walks to promote blood flow. Wearing compression stockings can also aid by applying gentle pressure to the legs, enhancing circulation.
Hydration supports blood flow by preventing thickening, making water an optimal choice for those at risk. Lifestyle changes like quitting smoking and incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines further help lower the likelihood of clot formation. Certain at-risk individuals may benefit from specific medical interventions. These include anticoagulant medications prescribed under professional supervision to reduce blood clotting risks.
Get Help With Deep Vein Thrombosis
Awareness of DVT, its risks, symptoms, and prevention methods enables better health choices. Prolonged immobility, underlying conditions, and lifestyle factors all play a role in promoting blood clot formation. Recognizing warning signs and adopting habits, such as regular movement and adequate hydration, can significantly reduce the likelihood of DVT. For individuals at higher risk, consult with healthcare professionals about tailored recommendations or interventions for your needs.







